Method overview
Instead of building world models into algorithms, we propose using large-scale multi-task world models as differentiable simulators for policy learning. When well-regularized, these models enable efficient policy learning with first-order gradient optimization. This allows PWM to learn to solve 80 tasks in < 10 minutes each without the need for expensive online planning.
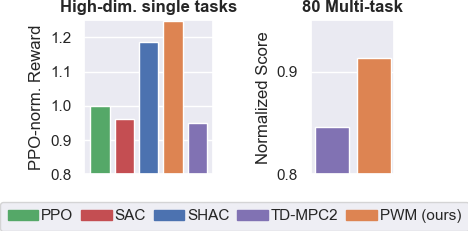
Single-task results
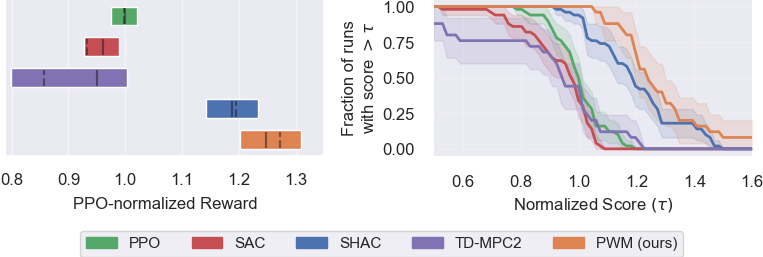
The figure shows 50% IQM with solid lines, mean with dashed lines, and 95% CI over all 5 tasks and 5 random seeds. PWM is able to achieve a higher reward than model-free baselines PPO and SAC, TDMPC2, which uses the same world model as PWM and SHAC which uses the ground-truth dynamics and reward functions of the simulator. These results indicate that well-regularized world models can smooth out the optimization landscape, allowing for better first-order gradient optimization.
Multi-task results
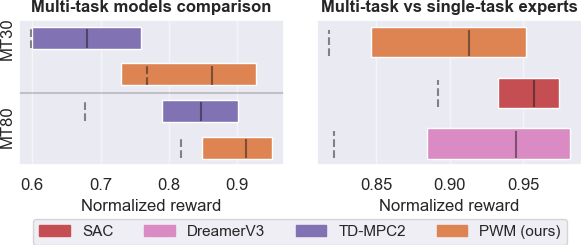
The figure shows the performance of PWM and TDMPC2 on 30 and 80 multi-task benchmarks with results over 10 random seeds. PWM is able to outperform TDMPC2 while using the same world model without any form of online planning, making it the more scalable approach to large world models. The right figure compares PWM, a multi-task policy, with single-task experts SAC and DreamerV3. It is impressive that PWM is able to match their performance while being multi-task and only trained on offline data.
We strongly believe that increasingly large world models of billions of parameters and policy learning strategies such as PWM can unlock dexterous robotics at scale.